Citric acid monohydrate
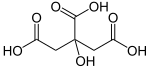
Citric acid is an organic compound with the formula C6H8O7. It is a colorless weak organic acid.It occurs naturally in citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, which occurs in the metabolism of all aerobic organisms.
More than two million tons of citric acid are manufactured every year. It is used widely as acidifier, flavoring, preservative, and chelating agent.
A citrate is a derivative of citric acid; that is, the salts, esters, and the polyatomic anion found in solutions and salts of citric acid. An example of the former, a salt is trisodium citrate; an ester is triethyl citrate.
Enquiry Form
Product Info
|
|||
 |
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Citric acid[1]
|
|||
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid[1]
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.973 | ||
| EC Number |
|
||
| E number | E330 (antioxidants, …) | ||
| KEGG | |||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
|
||
| UNII | |||
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C6H8O7 | |||
| Molar mass | 192.123 g/mol (anhydrous), 210.14 g/mol (monohydrate)[2] | ||
| Appearance | white solid | ||
| Odor | Odorless | ||
| Density | 1.665 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 1.542 g/cm3 (18 °C, monohydrate) |
||
| Melting point | 156 °C (313 °F; 429 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 310 °C (590 °F; 583 K) decomposes from 175 °C[3] | ||
| 54% w/w (10 °C) 59.2% w/w (20 °C) 64.3% w/w (30 °C) 68.6% w/w (40 °C) 70.9% w/w (50 °C) 73.5% w/w (60 °C) 76.2% w/w (70 °C) 78.8% w/w (80 °C) 81.4% w/w (90 °C) 84% w/w (100 °C)[4] |
|||
| Solubility | Soluble in acetone, alcohol, ether, ethyl acetate, DMSO Insoluble in C 6H 6, CHCl3, CS2, toluene[3] |
||
| Solubility in ethanol | 62 g/100 g (25 °C)[3] | ||
| Solubility in amyl acetate | 4.41 g/100 g (25 °C)[3] | ||
| Solubility in diethyl ether | 1.05 g/100 g (25 °C)[3] | ||
| Solubility in 1,4-dioxane | 35.9 g/100 g (25 °C)[3] | ||
| log P | −1.64 | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | pKa1 = 3.13[5] pKa2 = 4.76[5] pKa3 = 6.39,[6] 6.40[7] pKa4 = 14.4[8] |
||
|
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.493–1.509 (20 °C)[4] 1.46 (150 °C)[3] |
||
| Viscosity | 6.5 cP (50% aq. sol.)[4] | ||
| Structure | |||
| Monoclinic | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
|
Heat capacity (C)
|
226.51 J/(mol·K) (26.85 °C)[9] | ||
|
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
252.1 J/(mol·K)[9] | ||
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−1543.8 kJ/mol[4] | ||
| 1985.3 kJ/mol (474.5 kcal/mol, 2.47 kcal/g),[4] 1960.6 kJ/mol[9] 1972.34 kJ/mol (471.4 kcal/mol, 2.24 kcal/g) (monohydrate)[4] |
|||
| Pharmacology | |||
| A09AB04 (WHO) | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
|
Main hazards
|
Skin and eye irritant | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  [5] [5] |
|||
| Warning | |||
| H290, H319, H315[5] | |||
| P305+P351+P338[5] | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 155 °C (311 °F; 428 K) | ||
| 345 °C (653 °F; 618 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 8%[5] | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
3000 mg/kg (rats, oral) | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | HMDB (PDF) | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||






Reviews