Boric acid
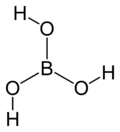
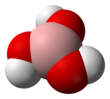
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula B(OH)3. It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolves in water, and occurs in nature as the mineral sassolite. It is a weak acid that yields various borate anions and salts, and can react with alcohols to form borate esters.
Boric acid is often used as an antiseptic, insecticide, flame retardant, neutron absorber, or precursor to other boron compounds.
The term “boric acid” is also used generically for any oxyacid of boron, such as metaboric acid HBO2 and tetraboric acid H2B4O7.
Enquiry Form
Product Info
|
|||
 |
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Boric acid
|
|||
| Other names
Orthoboric acid, Boracic acid, Sassolite, Borofax, Trihydroxyborane, Boranetriol, Hydrogen borate, Acidum boricum
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.114 | ||
| EC Number |
|
||
| E number | E284 (preservatives) | ||
| KEGG | |||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| BH3O3 | |||
| Molar mass | 61.83 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White crystalline solid | ||
| Density | 1.435 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 170.9 °C (339.6 °F; 444.0 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 300 °C (572 °F; 573 K) | ||
| 2.52 g/100 mL (0 °C) 4.72 g/100 mL (20 °C) 5.7 g/100 mL (25 °C) 19.10 g/100 mL (80 °C) 27.53 g/100 mL (100 °C) |
|||
| Solubility in other solvents | Soluble in lower alcohols moderately soluble in pyridine very slightly soluble in acetone |
||
| log P | −0.29 | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.24 (first proton), 12.4 (second), 13.3 (complete) | ||
| Conjugate base | Borate | ||
| −34.1·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Structure | |||
| Trigonal planar | |||
| 0 D | |||
| Pharmacology | |||
| S02AA03 (WHO) D08AD (WHO) | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 |
|||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | Nonflammable | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
2660 mg/kg, oral (rat) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Related compounds
|
Boron trioxide Borax |
||







Reviews